Osteochondrosis is the most common painful condition in humans. Most patients suffering from osteochondrosis learn about the presence of the disease when the destructive process in the cartilage tissues reaches the moment of serious changes with the involvement of nerve roots, which cause severe pain.
What kind of condition is this: "osteochondrosis of the spinal column" and how to treat it?
Osteochondrosis of the spine is a progressive pathological changes in the tissues of the spine, in particular the intervertebral discs and vertebral bodies with the involvement of the ligamentous apparatus of the spine in the painful process.
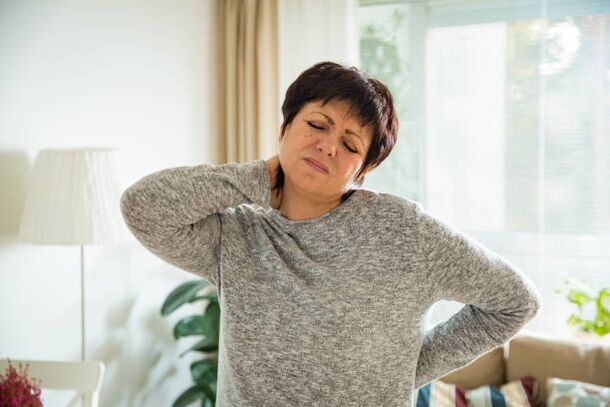

The collective term used in medical practice according to the international classification of diseases, denoting all forms of pathological conditions affecting the spine, is designated as "dorsopathy".
The destructive process develops for a long time, but it is possible to slow down and in some cases stop it, as well as to exclude the probable factors that caused the appearance of the disease. Patients are offered many options for the treatment of osteochondrosis, but without getting a result, they again and again look for who and where can help them.
Apitherapy
Treatment of osteochondrosis with apitherapy is quick, effective and cheap. Time has shown the high efficiency of bee venom in the treatment of various problems of the musculoskeletal system, in particular in the treatment of osteochondrosis. Apitherapy of osteochondrosis has been confirmed for centuries, but if earlier everything was reduced only to bee sting, today a large comprehensive program has been developed that allows you to influence all components of osteochondrosis, including predisposing factors and inhibit the possibility of the pathological process passing into protrusion and intervertebral groups.
The program includes:
- bee sting;
- API massages;
- stretching and traction of the spine;
- anti-inflammatory effects, including preparations and ointments based on honey, propolis, royal jelly, pollen;
- post-isometric relaxation;
- water rehabilitation;
- exercise complex yoga, etc.
Objectives of the spine therapy for the treatment of the spine:
- Elimination of pain and discomfort.
- Reducing inflammation.
- Relaxation of muscles.
- Regeneration of intervertebral discs.
- Restoration of trophism in the affected areas.
Apitherapy makes bone and cartilaginous tissue more "pliable" for mechanical, massage, manual and rehabilitation measures. Only in this case we can talk about real treatment, because if the spine is not prepared, then the possibilities are insufficient.
The complex of procedures, combined with sapitherapeutic treatment, enhances the already powerful effects of bee venom. One of the most ancient methods, is still one of the most effective for the restoration of our spine. With a wide variety of reasons for the development of osteochondrosis, no single method of exposure will give a full and long-term result, even bee venom requires powerful complex, restorative and rehabilitation support, in connection with which a special program was developed.
The minimum course is 5 days, the patient is in the clinic or comes for at least three hours (day hospital); involved a large group of specialists in various fields.
The reasons
Consider the reasons for the development of spinal osteochondrosis.
Age
This is due to a change in a number of processes associated with aging of the body, especially hormonal changes. Because of them, the bone tissue loses its density, becomes more porous, and reduces the elasticity of the discs themselves. The muscles of the spine weaken, poorly hold the vertebrae in the desired position, allowing the curvature of the spine. The nutrition of the vertebral tissues is deteriorating. All this entails an increased load on the intervertebral discs, their amortization capacity decreases, which leads to their rapid wear.
Spine injury
Today they are the reason for the development of osteochondrosis in young people, due to their hobbies for traumatic sports. About 90% of people who have received a spinal column injury in their lives will eventually face problems in the back.
Excess weight
The increased weight puts a greater load on the intervertebral discs, wearing them out faster, reducing the shock-absorbing properties, which subsequently leads to damage to the vertebral bodies, the formation of microcracks in them.
Hypodynamia
A very urgent problem in the modern world, when a person leads a slightly mobile lifestyle, especially with the introduction of computer technologies into everyday life. From school age, improper posture formation leads to curvature of the spine - scoliosis. This is also facilitated by the insufficient tone of the back muscles - a poorly formed muscle frame leads to a curvature of the spinal column and, as a result, the load on the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs is incorrectly redistributed. Insufficient blood circulation in certain parts of the spine due to a sedentary lifestyle contributes to the early development of degenerative changes in the vertebral tissue.
Genetic predisposition
There is a connection between anomalies in the development of the spinal column with certain genes. The emergence of early osteoporosis (bone depletion) and scoliosis is also genetically linked - markers of four genes responsible for hormonal levels, collagen production, assimilation of vitamin D and interleukin 6 have been identified. In addition, some gene locations are responsible for the strength and elasticity of the intervertebral discs.
Autoimmune diseases
"Breakdown" of the immune system can lead to the emergence of an autoimmune process with aggression, inflammation and subsequent destruction of the cartilaginous tissue of the intervertebral discs. Due to inflammatory processes, the elasticity and shock-absorbing properties of the discs are lost, which leads to the occurrence of osteochondrosis.
Endocrine diseases
Endocrine disorders, such as pathology of the thyroid gland, dysfunction of female sex hormones can negatively affect the elasticity of the intervertebral discs. Thyroid hormone thyroxine enhances the synthesis of collagen - the main structural substance of the disc. In case of insufficient thyroid function, the amortization properties of the disc are correspondingly reduced.
Stages
The mechanism of development of osteochondrosis. There are four successive stages of pathological changes in the intervertebral discs.
The first stage - before the onset of symptoms of the disease
The process of disc destruction starts from the nucleus pulposus. The height of the disc itself decreases and tears appear in the annulus fibrosus. But at this stage, the entire pathological process is limited only by the intervertebral disc. At this stage, no biochemical abnormalities are noted, clinical symptoms are absent or minimal. The first complaints of discomfort appear in a certain part of the spine, where the process of discopathy begins, and complaints of rapid fatigue of the back muscles may also appear.
The second stage is the progression of the process
The continuation of dystrophic changes in the intervertebral disc disrupts nutrition and metabolic processes in the nucleus pulposus. This leads to the death of cells of the gelatinous nucleus (necrosis), and in the future its complete destruction. At the same time, depletion continues in the annulus fibrosus due to the violation of its collagen structure. This affects the height of the intervertebral disc, reducing the space between the vertebral bodies. They become unstable, begin to displace along the plane, compressing the "flattened" disc and nearby nerve fibers even more.
The third stage is the destruction of the intervertebral disc
At this stage, the annulus fibrosus finally loses its cushioning properties, but the load on the spine remains the same, so many cracks and tears appear in the disc due to the incorrect distribution of collagen fibers. The annulus fibrosus is fragmented. By reducing the amortization properties, the load on the disc is redistributed and the compression in one area occurs more than in the other. The annulus fibrosus protrudes on one side and the nucleus pulposus is visible through it. This condition is called disc protrusion.
Stage four - hardening
During this period, the tissues of the dilapidated intervertebral disc "grow" with scar tissue, which is not elastic. It fills all microcracks in the annulus fibrosus. The process of sclerosing also involves other nearby vertebral tissues, especially the interspinous ligaments. Irreversible changes also occur in the nucleus pulposus, it is replaced by either fibrous tissue or cartilaginous tissue. unpleasant sensations.
Symptoms
In medical practice, three types of osteochondrosis are described according to its localization and symptoms - cervical, thoracic and lumbar.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
The symptoms of this form of osteochondrosis are explained by the structural features of the cervical spine, the passage of neurovascular bundles. Dystrophic changes in the annulus fibrosus are more often observed in the most mobile lower vertebrae at the level from C5 to C7. Typically, the formation of osteophytes on the lateral processes in the inner side, closer to a. Vertebralis, which leads to partial compression. This condition is identified by vertebral angiography. The main symptoms of this condition, caused by insufficient cerebral circulation, are dizziness associated with turning the head and bending the neck in certain directions.
The main reason for the compression of the nerve roots is a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc, due to a decrease in the vertical size.
The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are always pain. It can be dull in the form of heaviness in the neck or acute, shooting in the form of seizures In the clinical picture of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, in addition to the pain syndrome, so-called reflex syndromes are also observed. This is due to compression (compression) of the nerve root due to a decrease in the height and elasticity of the disc - especially the spinal roots and paravertebral sympathetic ganglia. And the most common compression syndrome is Naffziger's syndrome. This syndrome combines the lesion of the anterior scalene muscle and the radicular syndrome of the cervical spine, by compression of the brachial plexus and the subclavian artery. Clinically, it manifests itself in soreness of the anterior scalene muscle, its tension, pain in the shoulder girdle, shoulder, sensitivity disorders in the form of hyperesthesia, parasthesia and hyposthesia, muscle weakness in the arm, muscle hypotrophy of the shoulder girdle, swelling of the supraclavicular region.
Osteochondrosis and clinical syndromes of lesions of the thoracic spine
The thoracic spine has its own structural features, which cause the symptoms of osteochondrosis. In this part of the spine, in addition to axial load, rotational movements often occur. As a result of these movements, the anterior parts of the vertebral bodies and the anterior part of the intervertebral disc are worn out most often. In these areas, degenerative-dystrophic changes appear, salts are deposited very quickly, and spondylosis is formed. It affects the joints of the heads of the ribs and tubercles of the ribs - spondioarthrosis is formed. Due to the painful limitation of the chest, the organs of the chest begin to suffer and be affected.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are determined by damage to sympathetic nerve fibers and neuronal ganglia and disruption of the internal organs. Therefore, in the clinical picture of thoracic osteochondrosis, there are often sensitive disorders - hyperosthesia, parasthesia. They depend on the level of damage to nerve fibers and vertebrae. But all the same, despite the peculiarities of the symptom complex of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, the leading symptom is painful, which has its own characteristics: it increases at night, with vibration, cooling, turning the body to the sides, bending the body forward. Straightening the spine gives a feeling of fatigue in the muscles of the back. The characteristic symptoms of spondioarthrosis of the thoracic region are painful sensations that appear with a deep breath. It is located in the intercostal space, limiting respiratory movements. In the same way as in cervical osteochondrosis, the degenerative process in the thoracic vertebrae gives muscle tension in the corresponding section. But their feature - symmetrical muscle tension on both sides - is paravertebral.
Vegetative symptom complexincludes: increased pain sensitivity (hyperalgesia), increased temperature of a certain skin area, increased sweating (hyperhidrosis).
Vasomotor symptom complexcharacterized by disorders of the chest organs, especially the heart. In contrast to true coronary pain, pain in osteochondrosis increases with body turns, physical exertion.
Compression Syndromeis formed due to protrusion of discs and intervertebral hernias - compression of the nerve roots is manifested by girdle pain and a decrease in skin sensitivity in the corresponding vertebral segment.
Compression of the nerve roots from 5 to 10 of the thoracic vertebra can lead to disruption of the abdominal organs. At the same levels of root damage, intercostal neuropathies are also found. These are painful sensations in the intercostal space and a decrease in sensitivity in the projection of the compression of the root.
Clinical syndromes of lumbosacral osteochondrosis
The symptomatology of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine consists of two components: "vertebral" symptoms, due to the redistribution of the load on the lumbar vertebrae and symptoms of compression of the nerve roots, leading to impaired motor functions, sensory disorders.
The main sign and symptom of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is pain. They can be of different forms:
- Painful sensations, intense, in a separate area in the lumbar or sacral region - lumbago;
- Not acute, internal pain, aching in nature in the lumbar region, the area of the hip joint, knee or ankle - vegetative pain syndrome;
- Intense pain sensations with a return from the lumbosacral region to the piriformis muscle of the buttock along the sciatic nerve down to the sole - radicular syndrome due to compression of the sciatic nerve;
- Musculo-ligamentous pain, appears in the areas of attachment of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus to bone formations.
With the course of the disease, the physiological curves of the spine change - there may be an increase in lordosis in the lumbar region (hyperlordosis), kyphosis or scoliosis, a decrease in functional movements in the lumbosacral zone, muscle tension in certain zones.
Diagnostics
The most informative method for diagnosing osteochondrosis today is MRI, but radiography and ultrasound diagnostics can also confirm the presence of osteochondrosis, the only thing is that it is more difficult to clarify the severity of the diagnosis and say whether there are protrusions or hernias.
Treatment
"Hospital" medicine is not always able to help the patient with this diagnosis.
Traditional treatment is:
- ineffective conservative treatment;
- pain is blocked;
- prescribing massage, manual therapy, extracts without treatment;
- surgical intervention, which, of course, is a great risk to the body.